Type: Essential Amino Acid
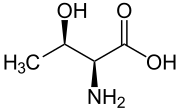
Name: Threonine (Thr, T), Chemical formula C4H9NO3
Importance- to Body:
Supports cardiovascular, liver, immune and central nervous system functions. Threonine keeps the elasticity between the connective heart tissues strong and healthy, speeds up the healing process in the body, is used to construct proteins, and builds strong enamel and bones.
Distribution- in Body:
Threonine is needed to create 2 amino acids (glycine and serine) which play a key role in producing elastin, muscle tissue, and collagen. Threonine aids in production of antibodies. The absorption of amino acids take place along the small intestine and free forms in the blood stream.
Excess Effects:
Nausea, Headaches, Upset Stomach, Difficulty Concentrating.
Deficiency Effects:
Fat build-up in the liver, Difficulty Digesting, Emotional Issues/Difficulties, Mood Swings, Depression, Anxiety.
Food Sources:
Fish, Poultry, Sesame Seeds, Lentils, Meats, Cottage Cheese, some Dairy Products.
Environmental/Geographic Sources:
Supplemental information:
Relative correlation between threonine and alleviating depression. Individuals on low protein diets or vegetarians should speak to a professional about options and supplements for threonine before use, although anyone can have a deficiency based on stress, infection, and age.
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Threonine
|
|
| Other names
2-Amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.704 |
| EC Number | 201-300-6 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C4H9NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 119.12 g·mol−1 |
| (H2O, g/dl) 10.6(30°),14.1(52°),19.0(61°) | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.63 (carboxyl), 10.43 (amino) |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH+
3 form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain containing a hydroxyl group, making it a polar, uncharged amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Threonine is synthesized from aspartate in bacteria such as E. coli. It is encoded by all the codons starting AC (ACT, ACC, ACA, and ACG).
Threonine sidechains are often hydrogen bonded; the most common small motifs formed are based on interactions with serine: ST turns, ST motifs (often at the beginning of alpha helices) and ST staples (usually at the middle of alpha helices).

