Type: Toxin
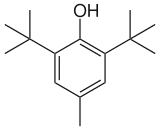
Name: Butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT)
RDA: 0
Importance- to Body:
Toxin: Respiratory, Eye, Skin, Other, Possible Carcinogen, FDA Classified as “acutely toxic”.
Distribution- in Body:
Skin, Respiratory System.
Excess Effects:
Skin Irritation, dangerous to eyes if physically exposed, Allergic Reactions
Deficiency Effects:
None Listed
Food Sources:
Cereal, Boxed Foods, Butter, Instant Mashed Potatoes, Chips, Wax Food Packaging, Shortening, Rubber, Plastic, Animal Foods, Cosmetics
Environmental/Geographic Sources:
Found in many Cosmetics, Hair Products, Deodorants, Sunscreen, Fragrances, Food
Supplemental information:
Synthetic, Preservative, Stabilizes Fat, Considered acutely toxic by the FDA, although there is disagreement. Prevents foods from becoming rancid, May be considered a carcinogen, Had negative effects on rats tested.
Works Cited:
“BHA and BHT: A Case for Fresh?” Scientific American, www.scientificamerican.com/article/bha-and-bht-a-case-for-fresh/.
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,6-Di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol | |
| Other names
2,6-Di-tert-butyl-p-cresol
3,5-Di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxytoluene DBPC BHT E321 AO-29 Avox BHT Additin RC 7110 Dibutylated hydroxytoluene 4-Methyl-2,6-di-tert-butyl phenol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.439 |
| EC Number | 204-881-4 |
| E number | E321 (antioxidants, ...) |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number | GO7875000 |
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H24O | |
| Molar mass | 220.36 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White to yellow powder |
| Odor | slight, phenolic |
| Density | 1.048 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 70 °C (158 °F; 343 K) |
| Boiling point | 265 °C (509 °F; 538 K) |
| 1.1 mg/L (20 °C) | |
| log P | 5.32 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.01 mmHg (20°C) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Flammable |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS signal word | Warning |
| H400, H410 | |
| P273, P391, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 127 °C (261 °F; 400 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
> 2,000 mg/kg (dermal, rat) |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
none |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 10 mg/m3 |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D. |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Butylated hydroxyanisole |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), also known as dibutylhydroxytoluene, is a lipophilic organic compound, chemically a derivative of phenol, that is useful for its antioxidant properties. European and U.S. regulations allow small amounts to be used as a food additive. In addition to this use, BHT is widely used to prevent oxidation in fluids (e.g. fuel, oil) and other materials where free radicals must be controlled.


