Type:Toxin
Name:Benzalkonium Chloride (BZK)
Importance- to Body:
Considered Acutely Toxic
Distribution- in Body:
Respiratory System, Skin, Area Applied
Excess Effects:
Dangerous for individuals with Eczema and Asthma, dangerous to eyes if physically exposed, can cause Rashes, Wheezing, Coughing, Allergic Reaction
Deficiency Effects:
None Listed
Food Sources:
None Listed
Environmental/Geographic Sources:
Household Products, Cleaning Products, Shampoos, Soaps, Deodorants, Perfumes, Eye Makeup
Supplemental information:
Inhaling BZK for long periods of time could cause asthma.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
N-Alkyl-N-benzyl-N,N-dimethylammonium chloride; Alkyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride; ADBAC; BC50 BC80; Quaternary ammonium compounds; quats
| |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.058.301 |
| EC Number | 264-151-6 |
| KEGG | |
| RTECS number | BO3150000 |
| UNII | |
| Properties | |
| variable | |
| Molar mass | variable |
| Appearance | 100% is white or yellow powder; gelatinous lumps; Solutions BC50 (50%) & BC80 (80%) are colorless to pale yellow solutions |
| Density | 0.98 g/cm3 |
| very soluble | |
| Pharmacology | |
| D08AJ01 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
EU classification (DSD) (outdated)
|
C, N |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R21/22, R34, R50 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | (S2), S36/37/39, S45, S61 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) (if solvent based) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
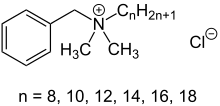
Benzalkonium chloride, also known as BZK, BKC, BAC, alkyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride and ADBAC, is a type of cationic surfactant. It is an organic salt classified as a quaternary ammonium compound. It has three main categories of use: as a biocide, a cationic surfactant, and as a phase transfer agent. ADBACs are a mixture of alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chlorides, in which the alkyl group has various even-numbered alkyl chain lengths.


