Type: Essential Amino Acid
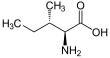
Name: Isoleucine (Ile), Chemical formula C6H12NO2
Importance- to body:
Supports blood clotting during a wound and aids in muscle repair, helps to improve stamina and increase energy levels, also regulating levels of blood sugar.
Distribution- in body:
Isoleucine is broken down in the muscle tissue to produce energy. Converted in the liver to blood sugar.
Excess effects:
Pellagra, kidney and liver failure, hypoglycemia.
Deficiency effects:
Dizziness, headaches, sleepiness/drowsiness, depression, irritability, disorientation and other symptoms similar to hypoglycemia.
Food Sources:
Meat, Fish, Eggs, Nuts, Seeds, Soybeans, Spirulina, Wheat germ, Legumes.
Environmental/Geographic Sources:
Supplemental information:
Should be paired with valine and leucine (three branched chain amino acids). Very important for athletes or body builders to take supplement to aid in healing of muscles, increase stamina, and boost energy.
Works Cited:
1. Garlick, and Peter J. “Nature of Human Hazards Associated with Excessive Intake of Amino Acids | The Journal of Nutrition | Oxford Academic.” OUP Academic, Oxford University Press, 1 Oct. 2004, academic.oup.com/jn/article/134/6/1633S/4688868.
2. “Branched-Chain Amino Acids: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Dosage, and Warning.”WebMD, WebMD, www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-1005/branched-chain-amino-acids.
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Isoleucine
|
|||
| Other names
(2S,3S)-2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.726 | ||
| KEGG | |||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C6H13NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 131.18 g·mol−1 | ||
| −84.9·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|||
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
||
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH+
3 form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a hydrocarbon side chain, classifying it as a non-polar, uncharged (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it, and must be ingested in our diet. Isoleucine is synthesized from pyruvate employing leucine biosynthesis enzymes in other organisms such as bacteria. It is encoded by the codons ATT, ATC, ATA.
Inability to break down isoleucine, along with other amino acids, is associated with the disease called Maple Syrup Urine Disease, which results in discoloration and a sweet smell in the patient's urine, which is where the name comes from. However, in severe cases, MSUD can lead to damage to the brain cells and ultimately death.