Type: Essential Amino Acid
Name: Phenylalanine (Phe, F), Chemical formula C9H11NO2
Importance- to Body:
A building block of protein, is being experimented for pain and adhd.
Distribution- in Body:
Enters liver and blood stream. After amino acids circulate the body they join with others during the breakdown and synthesis of tissue in the body. An amount of both essential amino acids and non-essential are needed for protein synthesis.
Excess Effects:
Heartburn, Headaches, Anxiety, Dizziness, Fatigue, Nausea, Jitteriness, Insomnia, Darkening of Skin, Nerve Damage, Hypertension, and High Blood Pressure.
Deficiency Effects:
Depression, Sluggish Metabolism, Confusion, Low Energy, Reduced Appetite, Vitiligo (a skin condition that causes skin to have light patches because skin loses its pigment), Difficulty Remembering Things.
Food Sources:
Meat, Eggs, Fish, Cheese, Liver, Soybeans.
Environmental/Geographic Sources:
Supplemental information:
Vitiligo is found to be maintained/treatable by taking Phenylalanine in combination with UVA exposure. Individuals with schizophrenia should not take phenylalanine. Schulze and Barbieri identified the compound in 1879 in yellow lupine seedlings. People with a rare disorder called phenylketonuria (PKU) need to stay clear from phenylalanine because it prevents them from metabolizing Phe.
 L-Phenylalanine
|
|
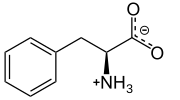 L-Phenylalanine at physiological pH
|
|
 3D phenylalanine model
|
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | US: /ˌfɛnəlˈæləniːn/, UK: /ˌfiːnaɪl-/ |
| IUPAC name
(S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.517 |
| KEGG | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
| Properties | |
| C9H11NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 165.19 g/mol |
| Acidity (pKa) | 1.83 (carboxyl), 9.13 (amino) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | See: data page |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an α-amino acid with the formula C
9H
11NO
2. It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of alanine. This essential amino acid is classified as neutral, and nonpolar because of the inert and hydrophobic nature of the benzyl side chain. The L-isomer is used to biochemically form proteins, coded for by DNA. Phenylalanine is a precursor for tyrosine, the monoamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), and the skin pigment melanin. It is encoded by the codons UUU and UUC.
Phenylalanine is found naturally in the breast milk of mammals. It is used in the manufacture of food and drink products and sold as a nutritional supplement for its reputed analgesic and antidepressant effects. It is a direct precursor to the neuromodulator phenethylamine, a commonly used dietary supplement. As an essential amino acid, phenylalanine is not synthesized de novo in humans and other animals, who must ingest phenylalanine or phenylalanine-containing proteins.


