Type: Compound
Vitamin: B5
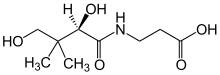
Name: Pantothenic Acid
RDA:10 mg
Importance- to Body:
Functions in form of coenzyme A in reactions that remove of transfer acetyl group, e.g., formation of acetyl CoA from pyruvic acid, oxidation and synthesis of fatty acids; also involved in synthesis of steroids and heme of hemoglobin.
Distribution- in Body:
Quite stable, little loss of activity with cooking except in acidic or alkaline solutions; liver, kidney, brain, adrenal, heart tissues contain large amounts.
Excess Effects:
None listed
Deficiency Effects:
(neuropathy of alcoholics is thought to be related to deficits).
Symptoms are vague: Loss of Appetite, Abdominal Pain, Mental Depression, Pains in Arms and Legs, Muscle Spasms, Neuromuscular Degeneration
Food Sources:
Widely distributed in animal foods, Whole Grains, Legumes, Liver, Yeast, Egg Yolk, Meat is an especially good source; some produced by enteric bacteria
Environmental/Geographic Sources:
None listed
Supplemental information:
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-[(2R)-2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanamido]propanoic acid
|
|
| Systematic IUPAC name
3-[(2R)-(2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanoyl)amino]propanoic acid
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | B00193 |
| 1727062, 1727064 (R) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.061 |
| EC Number | 209-965-4 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Pantothenic+Acid |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number | RU4729000 |
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C9H17NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 219.24 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow oil Colorless crystals (Ca2+ salt) |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.266 g/cm3 1.32 g/cm3 (Ca2+ salt) |
| Melting point | 183.83 °C (362.89 °F; 456.98 K) 196–200 °C (385–392 °F; 469–473 K) decomposes (Ca2+ salt) 138 °C (280 °F; 411 K) decomposes (Ca2+ salt, monohydrate) |
| Very soluble 2.11 g/mL (Ca2+ salt) |
|
| Solubility | Very soluble in C6H6, ether Ca2+ salt: Slightly soluble in alcohol, CHCl3 |
| log P | −1.416 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.41 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 9.698 |
|
Chiral rotation ([α]D)
|
+37.5° +24.3° (Ca2+ salt) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 287.3 °C (549.1 °F; 560.5 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
> 10 mg/g (Ca2+ salt) |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related alkanoic acids
|
Arginine Hopantenic acid 4-(γ-Glutamylamino)butanoic acid |
|
Related compounds
|
Panthenol |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Pantothenic acid, also called vitamin B5 (a B vitamin), is a water-soluble vitamin. Pantothenic acid is an essential nutrient. Animals require pantothenic acid in order to synthesize coenzyme-A (CoA), as well as to synthesize and metabolize proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. The anion is called pantothenate.
Pantothenic acid is the amide between pantoic acid and β-alanine. Its name derives from the Greek pantothen, meaning "from everywhere", and small quantities of pantothenic acid are found in nearly every food, with high amounts in fortified whole-grain cereals, egg yolks, liver and dried mushrooms. It is commonly found as its alcohol analog, the provitamin panthenol (pantothenol), and as calcium pantothenate.
Pantothenic acid was discovered by Roger J. Williams in 1933.


