Type: Essential Amino Acid
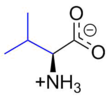
Name: Valine (V, Val) Chemical formula C5H11NO2
Importance- to Body:
Needed for muscle metabolism, maintaining proper amount of nitrogen in the body, and crucial for tissue repair. Valine may be beneficial in treating liver and gallbladder diseases (from the damage of drugs and alcohol).
Distribution- in Body:
Produces glucose and supplies after intense exercise to prevent break down of muscles.
Excess Effects:
Disruption of the kidneys or liver, headaches, dizziness.
Deficiency Effects:
Maple syrup urine disease is caused by the inability to metabolize valine, leucine, and isoleucine, lack of valine can affect the myelin coating of the nerves, and can cause neurological, motor and cognitive problems.
Food Sources:
Protein-Rich Foods (meat), Dairy Products, Soy Products, Legumes, Beans, Mushrooms, Leafy Green Vegetables.
Environmental/Geographic Sources:
Supplemental Information:
Closely related to leucine and isoleucine (similar function and structure). It is recommended that valine be taken with leucine and isoleucine for more convenience.
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Valine
|
|||
| Other names
2-Amino-3-methylbutanoic acid
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.703 | ||
| EC Number | 208-220-0 | ||
| KEGG | |||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C5H11NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 117.15 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.316 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 298 °C (568 °F; 571 K) (decomposition) | ||
| soluble | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.32 (carboxyl), 9.62 (amino) | ||
| -74.3·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|||
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
||
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Valine (symbol Val or V) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain isopropyl group, making it a non-polar aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Human dietary sources are foods that contain protein, such as meats, dairy products, soy products, beans and legumes. It is encoded by all codons starting with GU (GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG).
Like leucine and isoleucine, valine is a branched-chain amino acid. In sickle-cell disease, a single glutamic acid in β-globin is replaced with valine. Because valine is hydrophobic, whereas glutamic acid is hydrophilic, this change makes the hemoglobin prone to abnormal aggregation.